In spring 2019, the largest street renovation in Helsinki’s history began on Hämeentie. In addition to surface structures, the renovation project include water pipes, tram rails, cables and sewers. Protective structures beneath street level, in the roofing of the Sörnäinen metro station, have also been renovated. In the future, there will no longer be passenger vehicle through-traffic on the street, which is now intended for public transport, cyclists and pedestrians. Of course, driving into building yards will still be permitted. The urban environment, pipelines dating back to the early 20th century, and pedestrian and other traffic posed challenges of their own for the project.
Hämeentie is being renovated and built by Destia. We discussed the project and, more broadly, the gradual shift of street projects towards model-based production with Destia’s Development Manager, Mika Jaakkola, Hämeentie Project Chief Surveyor, Tatu Kallas, and Destia Automation Operator, Mikko Kansikas.
Hämeentie as a development project
The renovation on Hämeentie is now in its final stages. Chief Surveyor Kallas describes the progress made as follows:
“The end is already in sight. Around 99% of the tramway is ready. But there is still quite a bit to do in surface structures, for example.”
For Destia, the renovation of Hämeentie is its largest street construction project to date. In addition, more lessons have been learned about using model-based production.
For Destia, the renovation of Hämeentie is its largest street construction project to date. In addition, more lessons have been learned about using model-based production.
Model-based production refers to a new method and form of data transfer in infrastructure construction, in which construction-related plans are digitally available to everyone. Another key element of model-based production is the existence, in digital form, of construction process data and, for example, as-built models. Together, these allow for a comprehensive situational picture of the project. Infrakit is a project management system used in model-based production.
“The Hämeentie renovation has been a learning and development project in terms of model-based production. After all, the project planning was not model-based. However, we have studied how to introduce proven, functional practices, such as machine control and total station positioning, for roads in street construction. In addition, drone imaging and modelling are part of everyday life in the Hämeentie renovation project,” Jaakkola explains.
Urban construction differs from road construction
In comparison to roadway maintenance and construction, a great deal of attention must be paid to various traffic-related issues during urban construction.
“Traffic is a major factor, of course. During construction, we have to take people and traffic into account at all times. Then there is the existing infrastructure underground, including pipes and concrete structures,” Kallas explains.
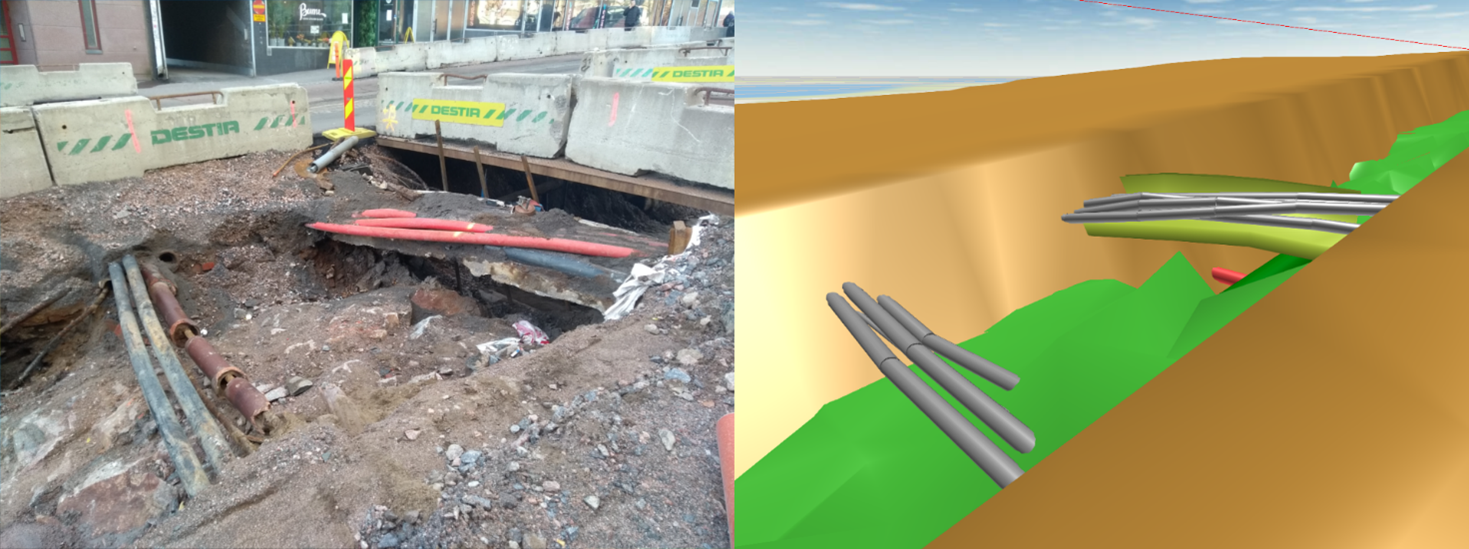
“Yes, they are the man-made things of the past that bring some very surprising twists and turns to today’s construction work. The difficulty is hugely increased by the fact that people started burying things underground in the early 20th century,” Kansikas adds.
However, not all findings are documented, as this would take up a lot of resources and time.
“Of course, we document all the structures that we handle. We also have a development project on a portion of one street, where we have surveyed and modelled all underground structures,” Kansikas describes.

Existing cables on the street measured and exported to the Infrakit combination model. Photo: Mikko Kansikas, Destia Oy.
Challenges and solutions for model-based production in an urban environment
Model-based production requires different skills to those deployed in traditional construction methods, and is still not used in all new projects. Plenty of plans are still prepared on paper. However, the model-based method enables 3D visualisation of the future structure, making it much easier to grasp the overall building. Planners also take centre stage in this new way of working.
“Model-based construction is not yet widely used, and we still have a lot to learn in this area, in order to build efficiently,” Kallas explains.
“Alliance projects also extensively allow for advance planning, data mapping, data transfer and cooperation. There is a lot of good in that,” Kansikas says.
“Construction sites often grind to a halt if you can’t get a fast answer to something. The alliance model is one solution to this challenge. During cooperation, the initial data can be mapped more comprehensively, enabling higher-quality model-based planning and production. For example, we are involved in the Kalasatama-to-Pasila project, which is based on an alliance model,” Jaakkola says.
Using digital information in traditional construction processes
Destia used Infrakit for data management in the Hämeentie project.
“Infrakit is a great platform to which items such as background maps, plans and drone images can be added,” Kansikas explains.
“Infrakit is a great platform to which items such as background maps, plans and drone images can be added.” – Mikko Kansikas
“Images are used a great deal in construction and are very useful. However, drone images are better than traditional photos, as they are more informative. One person may take around 5,000 photographs over the course of 18 months on a project, which is several hundred per month. When you use a drone to take, say, orthophotos or aerial photographs over a kilometre of terrain every two weeks, you learn a great deal about the overall development of the site,” Kallas says.
“By utilising Infrakit, plans and models can be made available to the entire project organisation, from project management to builders installing piping. Fewer mistakes are made when those involved in a project have up-to-date plans at their fingertips. Furthermore, digital information can be used in traffic management and project management in general,” Jaakkola adds.

The planned new pipeline will collide with existing infrastructure. Infrakit makes it easy to adjust the plan before implementation. Photo: Mikko Kansikas, Destia Oy.
Fostering closer cooperation in data management
Further development is currently required in data management and the sharing of information between design and construction. Many individual details and measured lines and points are still being sent between project actors.
“If there were model-based plans, we could build more rationally. There are no problems with the machines themselves, the models can be transferred to excavators,” Kallas explains.
“There is still a need for development on the street construction side in this respect,” Jaakkola adds.
“At Infrakit, the information is readily available. There are also plenty of opportunities that can be exploited when building with model-based design. We know what to do,” Kallas says.
“Information travels faster between actors,” Kallas sums up.
It is easy to see the overall benefits of a real-time cooperation model and platform for planning and implementation in roadway and street maintenance. Infrakit’s visual nature makes it easier to solve problems: it provides the same view on home-office displays as would be possible on-site.
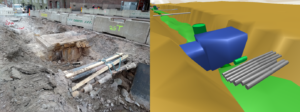
Adapting the new to the old virtually with a browser. Photo: Mikko Kansikas, Destia Oy.
Model-based production renews infrastructure construction
Finland and the Nordic countries have made huge strides forward in model-based construction.
“We have come quite far in this, especially in Finland and the Nordic countries. Model-based production makes a number of things possible; construction will be of higher quality, less expensive and more sensible,” Jaakkola describes.
“Our work will be more efficient and we will have a much clearer overall picture of projects,” Kallas adds.
“I would add that operating through a model-based method allows us to plan work more efficiently and reduce emissions,” Jaakkola says.
“I would add that operating through a model-based method allows us to plan work more efficiently and reduce emissions.” – Mika Jaakkola
“Although the Hämeentie renovation project was not totally model-based, much has been learned along the way, and we have become more familiar with Infrakit. We have tried to gather best practices from model-based production for this project as well. Infrakit has also developed new tools for us, which we have been able to use. In general, I would say that we just have to take the decision to work with model-based planning in various projects. It’s easy to move forward when developers complete a smooth pilot and have good experiences,” Kallas says.
“Although the Hämeentie renovation project was not totally model-based, much has been learned along the way, and we have become more familiar with Infrakit. We have tried to gather best practices from model-based production for this project as well.” – Tatu Kallas
“The same initial challenges were faced in road construction, but this area has moved further forward and new practices have been learned. People are often wary of new things and it can feel difficult to discard what has worked before,” Jaakkola adds.
“Growing pains will be unavoidable for a while, but I think that everyone should use the same model to avoid the fragmentation of work and knowledge,” Kallas says.
“In addition, we already have work to do and the required know-how, and are able to use model-based planning – it’s not a problem,” Jaakkola says.
“To sum up, we have found that model-based production works at Destia, and it’s a big deal that we can also use it for urban construction in the future. Planning still plays a central role and new methods can speed up turnaround times and reduce costs,” Jaakkola summarises.

 ‘Stick to what you know’
‘Stick to what you know’











Recent Comments